Problem
You are given an integer array prices where prices[i] is the price of a given stock on the ith day.
On each day, you may decide to buy and/or sell the stock. You can only hold at most one share of the stock at any time. However, you can buy it then immediately sell it on the same day.
Find and return the maximum profit you can achieve.
Example 1:
Input: prices = [7,1,5,3,6,4]
Output: 7
Explanation: Buy on day 2 (price = 1) and sell on day 3 (price = 5), profit = 5-1 = 4.
Then buy on day 4 (price = 3) and sell on day 5 (price = 6), profit = 6-3 = 3.
Total profit is 4 + 3 = 7.
Example 2:
Input: prices = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: 4
Explanation: Buy on day 1 (price = 1) and sell on day 5 (price = 5), profit = 5-1 = 4.
Total profit is 4.
Approach & Explanation
The problem asks for the maximum profit by buying and selling multiple times. This can be solved using a Greedy Algorithm.
The “Peak-Valley” Approach
If you visualize the stock prices as a chart, you’ll see peaks and valleys. The key insight is: Assuming we can trade as many times as we want, the maximum profit is simply the sum of all upward slopes.
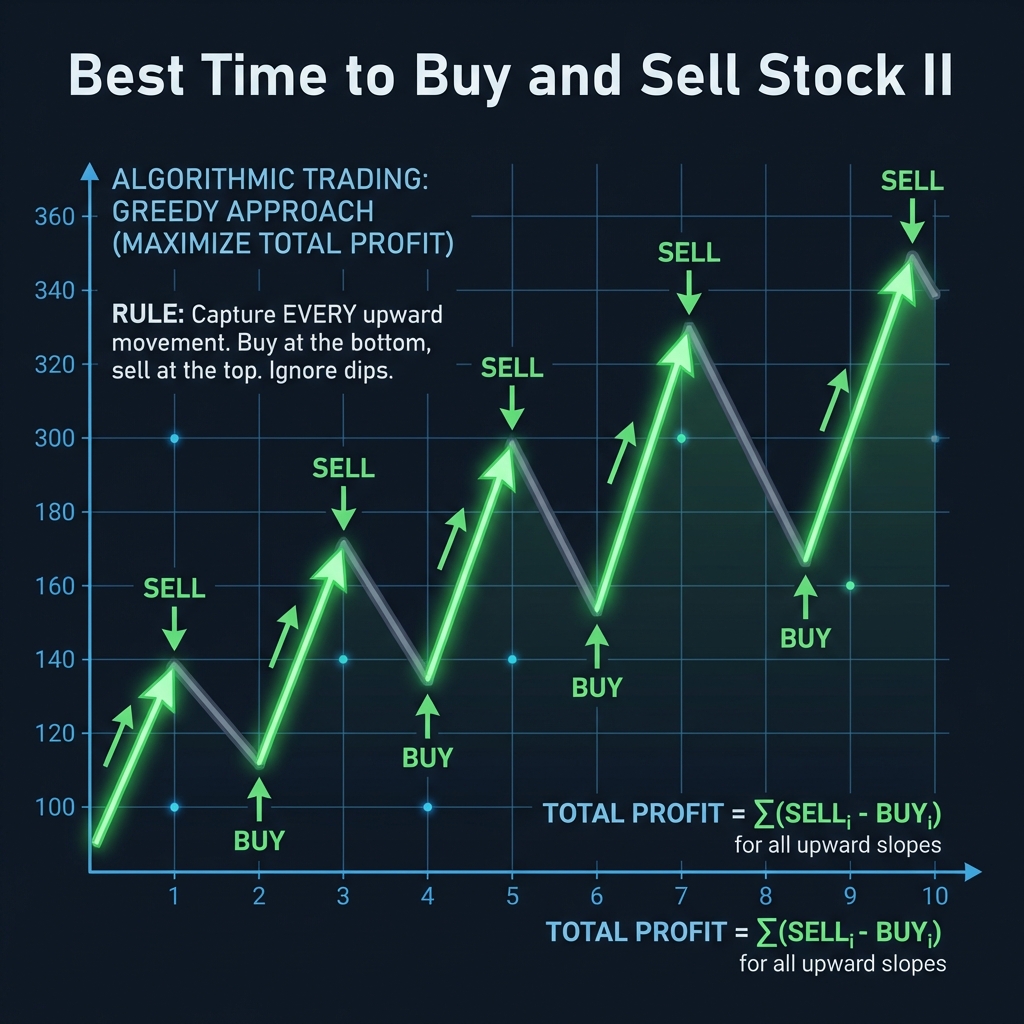
- We don’t need to find the absolute lowest buying point and absolute highest selling point.
- Instead, if the price tomorrow is higher than today (
prices[i] > prices[i-1]), we “buy” today and “sell” tomorrow to capture that profit. - We repeat this for every day.
Complexity:
- Time:
O(n)- We pass through the array once. - Space:
O(1)- No extra space used.
Solution
Java
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int profit = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < prices.length; i++) {
if(prices[i] > prices[i-1]) {
profit += (prices[i] - prices[i-1]);
}
}
return profit;
}
}
Go
func maxProfit(prices []int) int {
profit := 0
for i := 1; i < len(prices); i++ {
if prices[i] > prices[i-1] {
profit += prices[i] - prices[i-1]
}
}
return profit
}