Problem
Given an integer array nums, return true if any value appears at least twice in the array, and return false if every element is distinct.
Example 1:
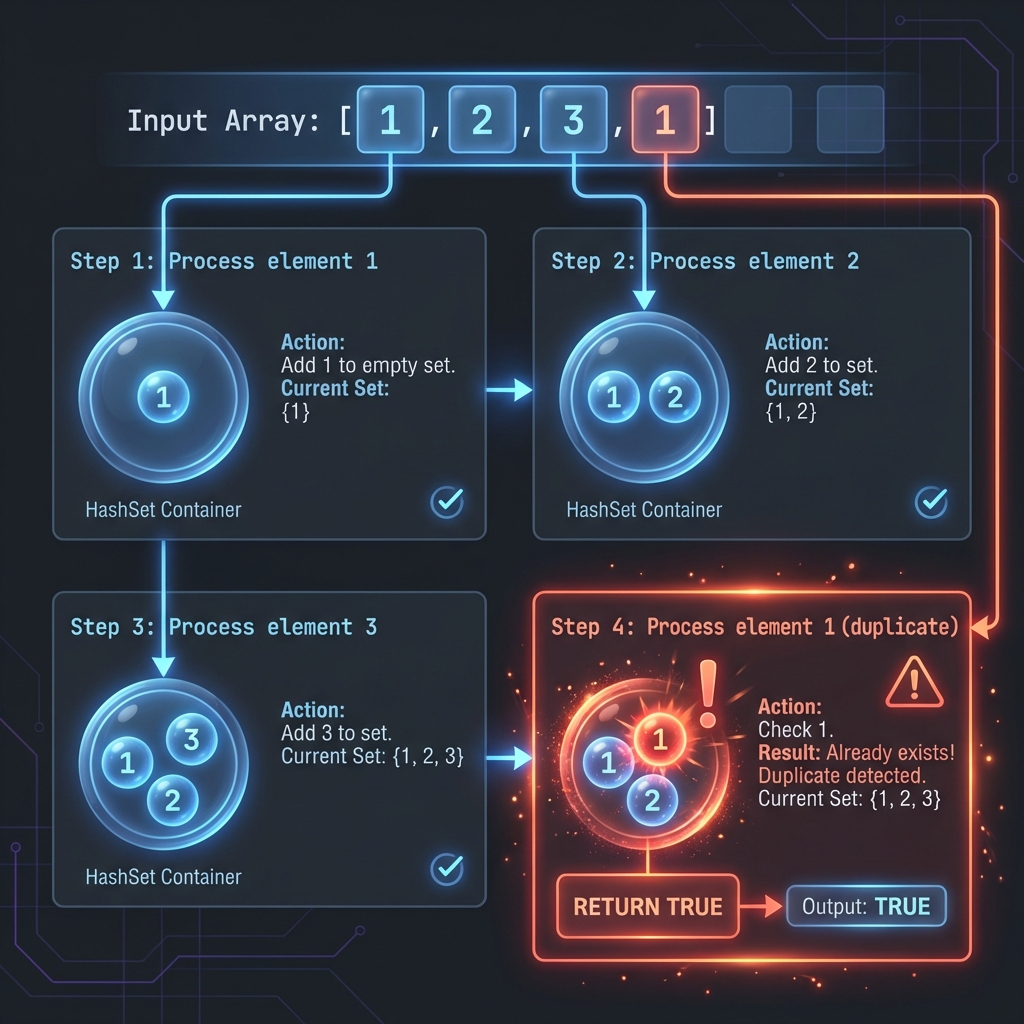
Input: nums = [1,2,3,1]
Output: true
Explanation: The element 1 occurs at the indices 0 and 3.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,4]
Output: false
Explanation: All elements are distinct.
Example 3:
Input: nums = [1,1,1,3,3,4,3,2,4,2]
Output: true
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 10^5-10^9 <= nums[i] <= 10^9
Approach & Explanation
The optimal approach uses a HashSet to track elements we’ve seen:
- Iterate through the array
- For each element, check if it’s already in the set
- If yes → return
true(duplicate found) - If no → add it to the set
- If we finish the loop without finding duplicates → return
false
Complexity Analysis
- Time: O(n) - single pass through the array
- Space: O(n) - worst case, all elements are unique
Alternative Approaches
- Sorting: Sort the array, then check adjacent elements. O(n log n) time, O(1) space.
- Brute Force: Compare every pair. O(n²) time, O(1) space.
Solution
Java
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.HashSet;
class Solution {
public boolean containsDuplicate(int[] nums) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
for(int num : nums) {
if(set.contains(num)) {
return true;
}
set.add(num);
}
return false;
}
}
Go
func containsDuplicate(nums []int) bool {
set := make(map[int]struct{}, len(nums))
for _, num := range nums {
if _, exists := set[num]; exists {
return true
}
set[num] = struct{}{}
}
return false
}
Key Insight
The HashSet provides O(1) average time complexity for both contains() and add() operations, making this the most efficient solution for this problem.