Module 5: Graphs
Graph Basics
A Graph is a non-linear data structure consisting of Vertices (nodes) and Edges (connections between vertices). It is the most general structure used to model networks (social networks, maps, internet).
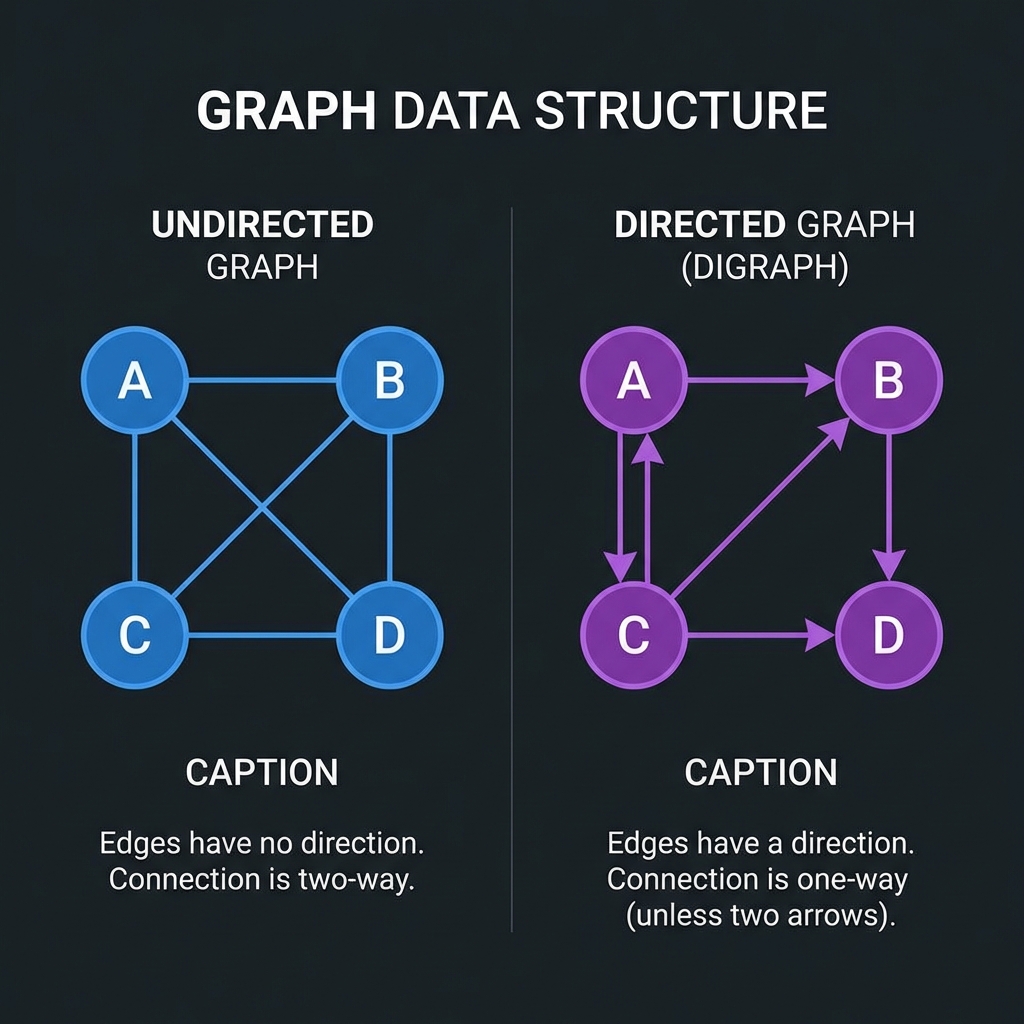
Types of Graphs
- Directed (Digraph): Edges have a direction (A → B).
- Undirected: Edges have no direction (A — B).
- Weighted: Edges have values/weights (useful for shortest path).
- Cyclic/Acyclic: Whether the graph contains loops.
Representing Graphs
- Adjacency Matrix: A 2D array.
matrix[i][j] = 1if edge exists. Good for dense graphs. O(1) lookup. - Adjacency List: Array of Lists.
adj[i]contains all neighbors ofi. Good for sparse graphs. O(V+E) traversal.
Problems
(No problems added yet)