Module 3: Linked Lists
Linked List Basics
A Linked List is a linear data structure where elements are not stored in contiguous memory locations. Instead, each element (node) points to the next using a pointer or reference.
Types of Linked Lists
- Singly Linked List: Each node points to the next node. Traversal is one-way.
- Doubly Linked List: Each node has two pointers:
nextandprev. Traversal is two-way. - Circular Linked List: The last node points back to the head.
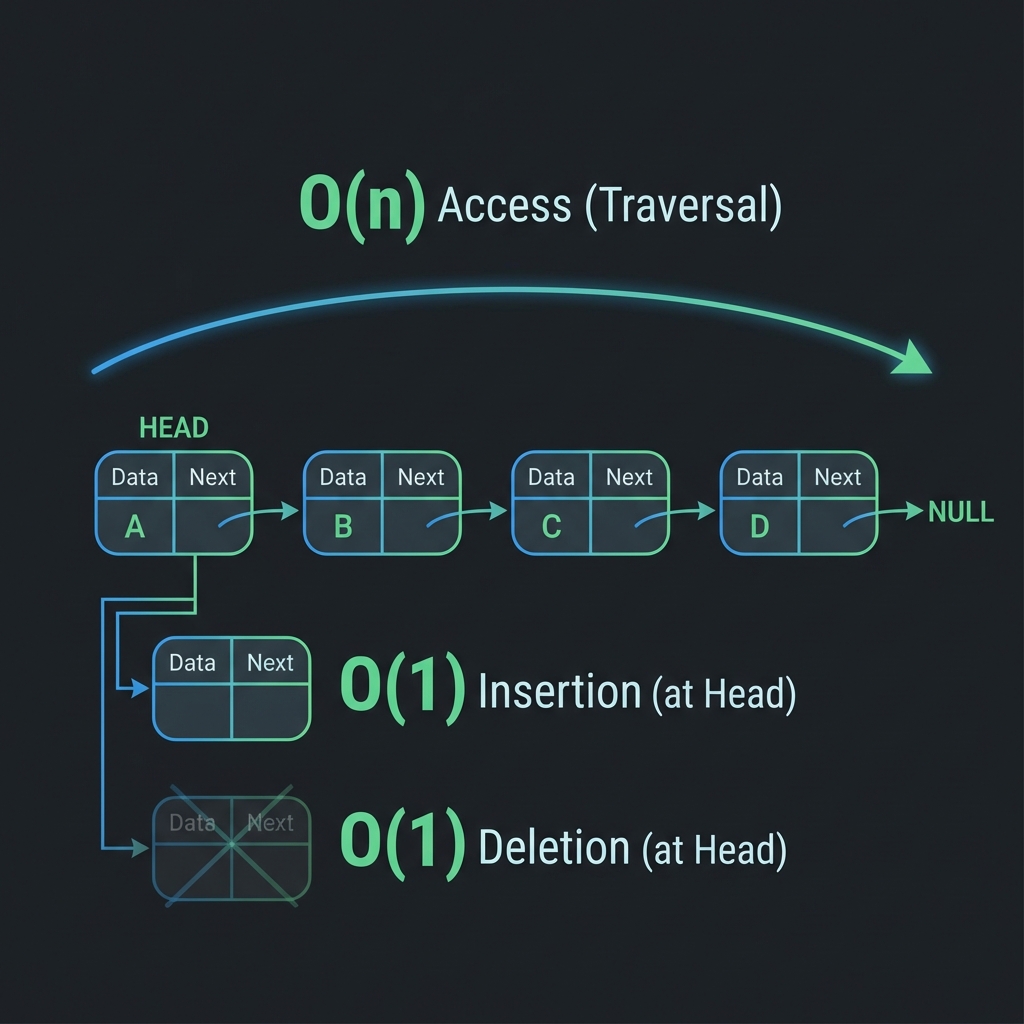
Time Complexity
| Operation | Complexity | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Access | O(n) | Must traverse from head |
| Insertion (at Head) | O(1) | Just update pointers |
| Insertion (at End) | O(n) | Unless you have a tail pointer |
| Deletion (at Head) | O(1) |
Problems
(No problems added yet)