Problem
Given an integer array nums sorted in non-decreasing order, remove the duplicates in-place such that each unique element appears only once. The relative order of the elements should be kept the same.
Consider the number of unique elements in nums to be k. After removing duplicates, return the number of unique elements k.
The first k elements of nums should contain the unique numbers in sorted order. The remaining elements beyond index k - 1 can be ignored.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,1,2]
Output: 2, nums = [1,2,_]
Explanation: Your function should return k = 2, with the first two elements of nums being 1 and 2 respectively.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [0,0,1,1,1,2,2,3,3,4]
Output: 5, nums = [0,1,2,3,4,_,_,_,_,_]
Explanation: Your function should return k = 5, with the first five elements of nums being 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 respectively.
Visualizing Duplicate Removal
Watch how the two-pointer technique identifies and removes duplicates:
k (Writer)
i (Reader)
Starting: k=1 (first element always unique)
Approach & Explanation
Since the array is sorted, all duplicate elements will be next to each other. We can use the Two-Pointer Technique to solving this efficiently in linear time O(n) and constant extra space O(1).
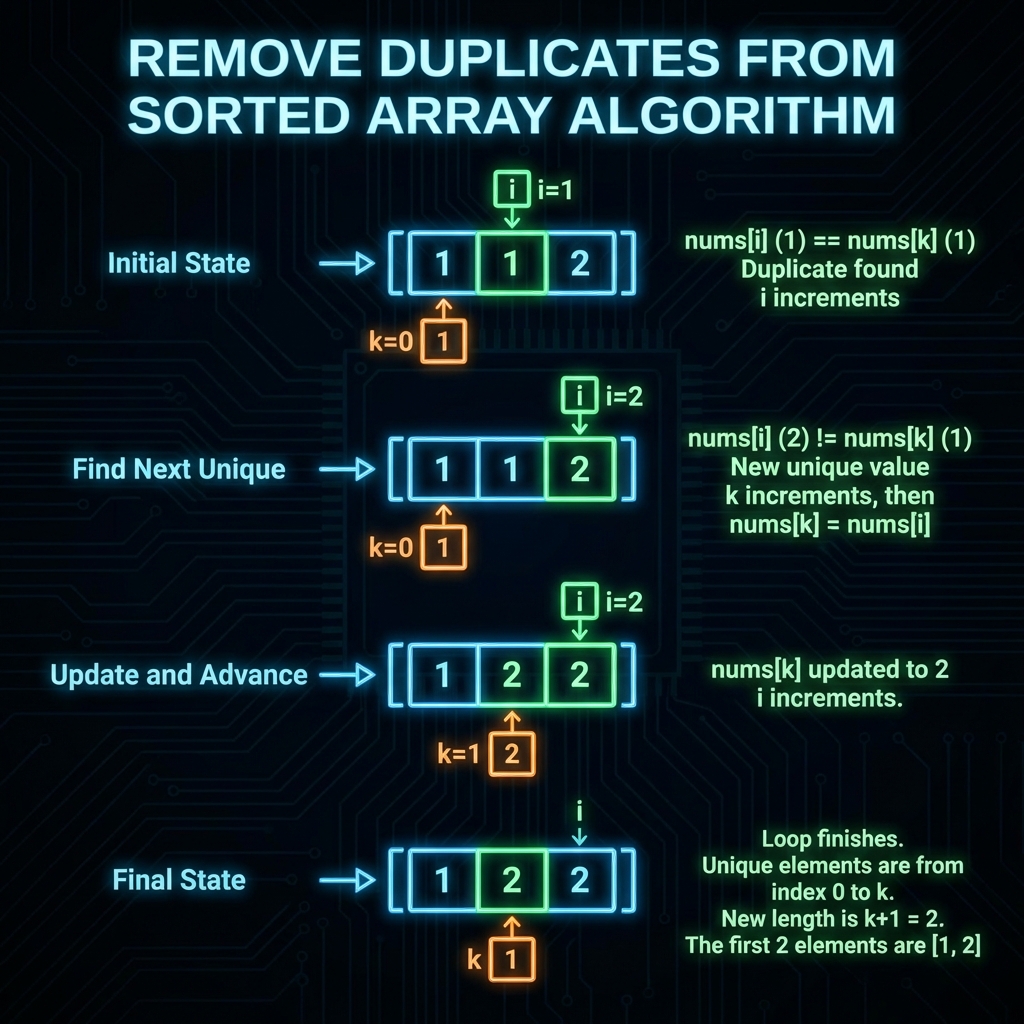
The Two Pointers
k(The “Writer”): Points to the index where the next unique element should be written. It basically tracks the length of the unique prefix.i(The “Reader”): Scans through the array from left to right.
Algorithm
- Start
kat1(since the first element at index0is always unique). - Iterate
istarting from1up to the end of the array. - Compare
nums[i]with the previous written unique element (or simplynums[i-1]in the original array context, but conceptually we are comparingcurrentvsprevious). - If
nums[i]is different fromnums[i-1], we have found a new unique number.- Write it to
nums[k]. - Increment
k.
- Write it to
- If
nums[i]is the same, it’s a duplicate. We ignore it and just incrementi. - Finally, return
k, which represents the count of unique elements.
Solution
Java
class Solution {
public int removeDuplicates(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length == 0) return 0;
int k = 1; // Index of the next unique element
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] != nums[i - 1]) {
nums[k] = nums[i];
k++;
}
}
return k;
}
}
Go
func removeDuplicates(nums []int) int {
if len(nums) == 0 {
return 0
}
k := 1
for i := 1; i < len(nums); i++ {
if nums[i] != nums[i-1] {
nums[k] = nums[i]
k++
}
}
return k
}