Problem
Given an integer array nums, rotate the array to the right by k steps, where k is non-negative.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7], k = 3
Output: [5,6,7,1,2,3,4]
Explanation:
rotate 1 steps to the right: [7,1,2,3,4,5,6]
rotate 2 steps to the right: [6,7,1,2,3,4,5]
rotate 3 steps to the right: [5,6,7,1,2,3,4]
Example 2:
Input: nums = [-1,-100,3,99], k = 2
Output: [3,99,-1,-100]
Explanation:
rotate 1 steps to the right: [99,-1,-100,3]
rotate 2 steps to the right: [3,99,-1,-100]
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 10^5-2^31 <= nums[i] <= 2^31 - 10 <= k <= 10^5
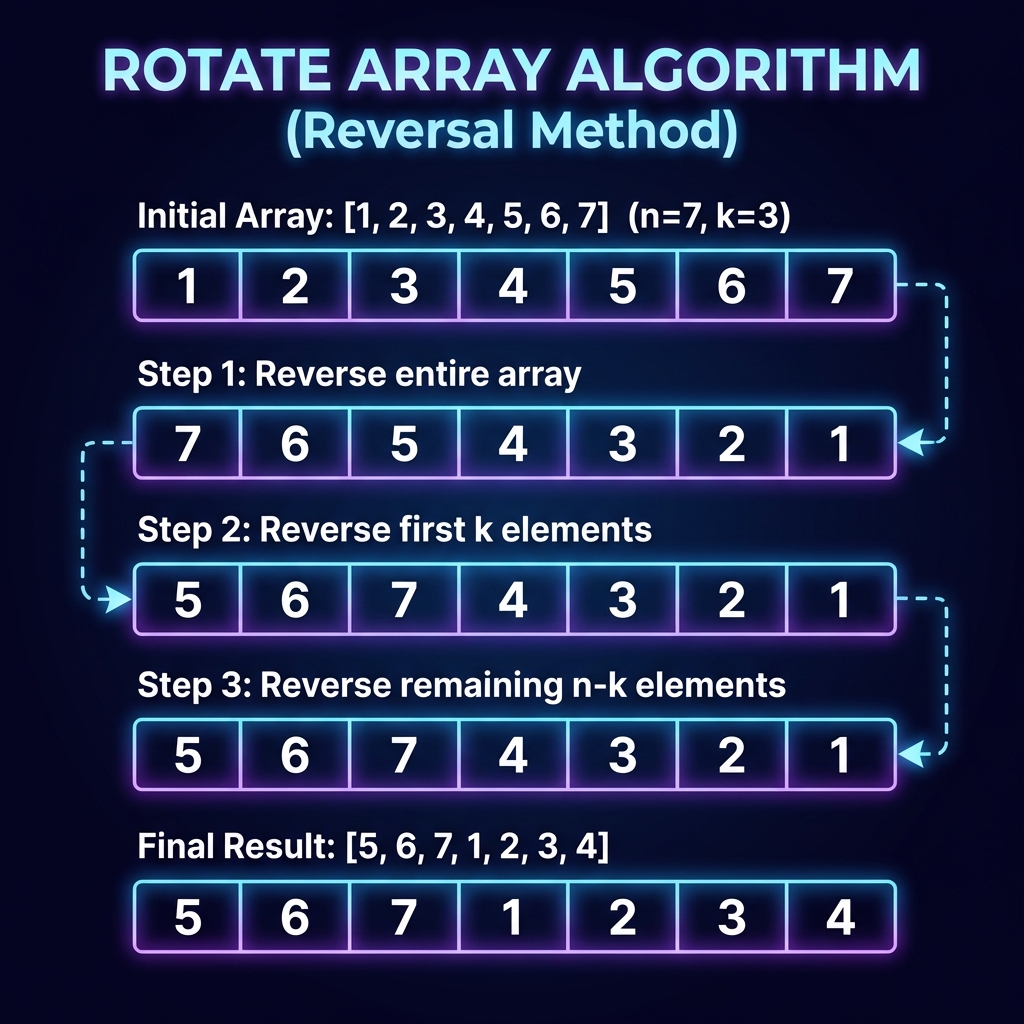
Visualizing the Reversal Algorithm
See how the three-step reversal trick rotates the array in-place:
Initial array: [1,2,3,4,5,6,7], k=3
Approach & Explanation
There are two primary ways to solve this in O(1) extra space:
1. The Reversal Algorithm (Popular)
This is the most intuitive “trick” solution:
- Reverse the entire array.
- Reverse the first
kelements. - Reverse the remaining
n-kelements.
2. Cyclic Replacements (Juggling Algorithm)
This approach moves each element directly to its target index. Since moving one element displaces another, we “pick up” the displaced element and move it to its new target, continuing this cycle until we return to the starting index. We repeat this for multiple cycles if necessary until all elements have been moved.
Note: Always handle the case where k > nums.length by doing k = k % nums.length.
Solution
Java (Cyclic Replacements)
class Solution {
public void rotate(int[] nums, int k) {
int n = nums.length;
k %= n;
if (k == 0) return;
int count = 0;
for (int start = 0; count < n; start++) {
int prev = nums[start];
int curr = start;
do {
int next = (curr + k) % n;
int temp = nums[next];
nums[next] = prev;
prev = temp;
curr = next;
count++;
} while (start != curr);
}
}
}
Go (Cyclic Replacements)
func rotate(nums []int, k int) {
n := len(nums)
if n == 0 {
return
}
k %= n
if k == 0 {
return
}
count := 0
for start := 0; count < n; start++ {
curr := start
prev := nums[curr]
for {
next := (curr + k) % n
temp := nums[next]
nums[next] = prev
prev = temp
count++
curr = next
if start == curr {
break
}
}
}
}
Alternative: Reversal Algorithm
Java
class Solution {
public void rotate(int[] nums, int k) {
int n = nums.length;
k %= n;
reverse(nums, 0, n - 1);
reverse(nums, 0, k - 1);
reverse(nums, k, n - 1);
}
private void reverse(int[] nums, int start, int end) {
while (start < end) {
int temp = nums[start];
nums[start] = nums[end];
nums[end] = temp;
start++;
end--;
}
}
}