Problem
Given a non-empty array of integers nums, every element appears twice except for one. Find that single one.
You must implement a solution with a linear runtime complexity and use only constant extra space.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [2,2,1]
Output: 1
Example 2:
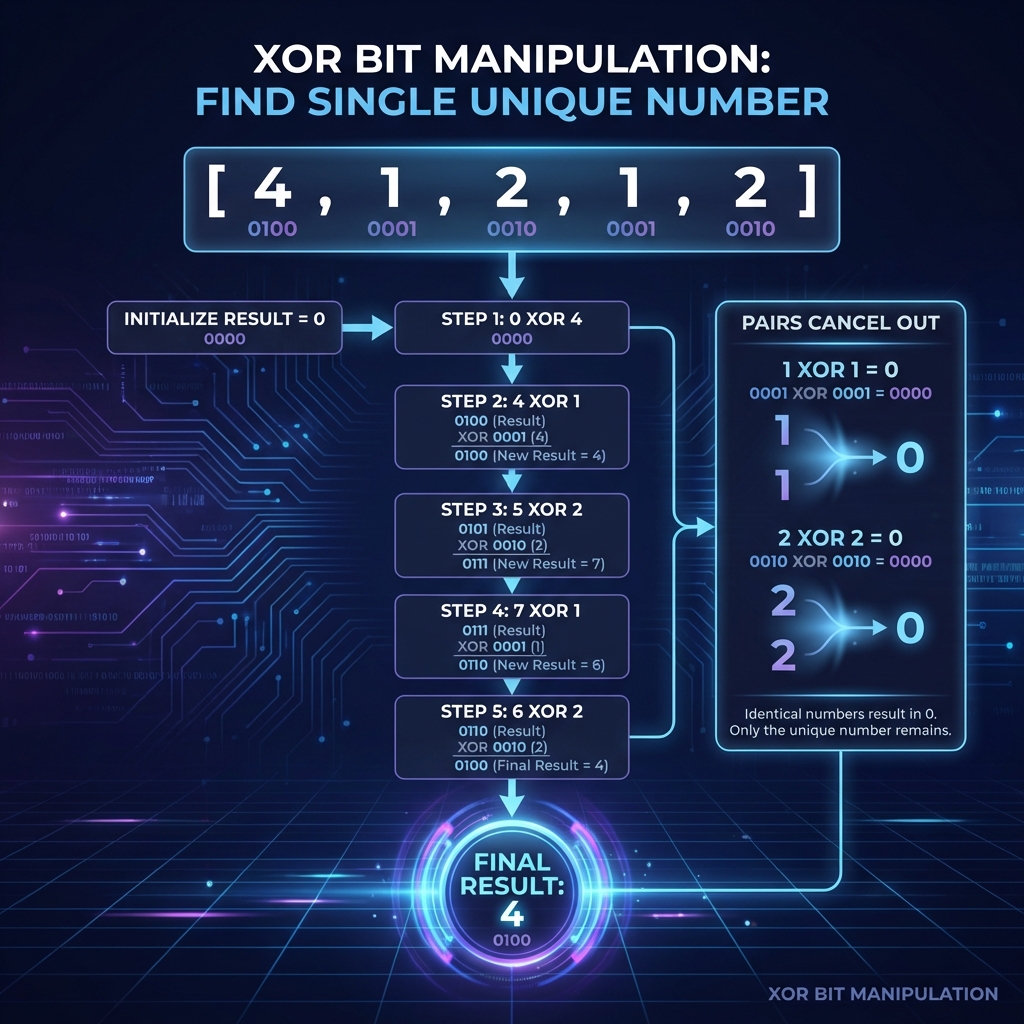
Input: nums = [4,1,2,1,2]
Output: 4
Example 3:
Input: nums = [1]
Output: 1
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 3 * 10^4-3 * 10^4 <= nums[i] <= 3 * 10^4- Each element appears twice except for one element which appears only once.
Approach & Explanation
This is a classic problem that demonstrates the power of bit manipulation.
XOR Properties
The XOR (^) operator has these key properties:
- Self-cancellation:
a ^ a = 0 - Identity:
a ^ 0 = a - Commutativity:
a ^ b = b ^ a - Associativity:
(a ^ b) ^ c = a ^ (b ^ c)
Algorithm
If we XOR all numbers together:
- Pairs cancel out:
2 ^ 2 = 0 - The single number remains:
0 ^ 4 = 4
Example: [4, 1, 2, 1, 2]
4 ^ 1 ^ 2 ^ 1 ^ 2
= 4 ^ (1 ^ 1) ^ (2 ^ 2)
= 4 ^ 0 ^ 0
= 4
Complexity Analysis
- Time: O(n) - single pass
- Space: O(1) - only one variable
Solution
Java
class Solution {
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
int ans = 0;
for(int num : nums) {
ans ^= num;
}
return ans;
}
}
Go
func singleNumber(nums []int) int {
a := 0
for _, num := range nums {
a ^= num
}
return a
}
Key Insight
This problem perfectly meets the O(n) time and O(1) space constraints by leveraging the mathematical properties of XOR. This is a must-know pattern for bit manipulation problems!